Report Overview
Featuring 52 tables and 69 figures – now available in Excel and Powerpoint! Learn More

Global demand for healthcare disinfectants and cleaning chemicals is expected to rise 4.3% per year to $4.6 billion in 2026, supported by:
- global increases in healthcare spending, most notably in developing regions
- the growing number of medical facilities to meet the needs expanding urban populations
- ongoing introductions of products that are formulated to be effective against broader spectrums of pathogens and that are more environmentally safe
- efforts to combat the threat of healthcare-associated infections and to prevent the emergence of more disinfectant-resistant bacteria
While growth will be healthy, it will come off a relatively high 2021 base that resulted from more frequent and stringent cleaning protocols and the resumption of regular health and dental care that had been postponed in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Development of Healthcare Services in the Asia/Pacific Region Drives Global Growth
Significant opportunities for new sales exist in developing countries throughout the Asia/Pacific region, as the movement of populations into more crowded urban settings and the construction of healthcare facilities leads to more widespread usage of healthcare disinfectants and cleaning chemicals. The market will benefit not only from the expanding number of facilities and patients, but also by more intensive use of products in these facilities. As patient volumes rise, so does the need to reduce the risk of HAIs.
China in particular continues to offer significant opportunities for new sales. Although increases in healthcare spending are no longer booming, they continue to advance at a rapid pace. The country’s large population continues to urbanize, and as more consumers in the country have disposable income and access to healthcare, they are looking for higher quality healthcare with more stringent sanitation protocols and are more likely to invest in elective procedures. Additionally, China’s zero-COVID policy will have an impact on demand for disinfectants and cleaners in the near term, as increased testing – and the increased utilization of healthcare facilities where testing is performed – boosts demand.
Opportunities Still Found in Established Healthcare Sectors
In contrast to the Asia/Pacific and Africa/Mideast regions, the healthcare markets of the US, Japan, and Western Europe are much more mature, but there remain opportunities for sales in these areas. As populations age, healthcare services are more widely used, and elder care facilities are expanding. Cleaning regimens are of particular importance in elder care settings, where residents are among the groups that remain most at risk from a variety of transmissible illnesses.
The ongoing development and uptake of better performing products that are easier to use and are more environmentally friendly will also support demand. However, stronger gains will be limited by the introduction of systems intended to reduce costs, as well as the growing use of novel technologies such as UV light and ozone in lieu of chemical cleaners.
Hand Cleansers Versus Hand Sanitizers
For this study, hand cleansers are defined as I&I hand cleansers that are applied to the hands and physically remove dirt, soil, and pathogens from the skin. Hand cleansers can be formulated with pure soap tallow, synthetic detergents, or soap-detergent combinations; they are marketed in solid (bar), liquid, cream, paste, powder, and waterless forms. Most of these hand cleaners are similar in content to household hand cleaners. However, specialized antimicrobial products – such as surgical scrubs – are used in healthcare settings, although triclosan (a common antibacterial ingredient in hand cleansers) has been linked to antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
In contrast, hand sanitizers kill pathogens but do not remove them from the skin, thereby lowering the number but not eliminating the pathogens entirely. Hand sanitizers come in liquid and gel forms, frequently utilize ethanol or isopropanol as the primary sanitizing agent, and can include fragrances and emollients.
While hand cleansers are included in the other cleaning chemicals product class in the present study, hand sanitizers are included in the disinfectants and sanitizers product class.
Both product types are widely used in healthcare settings. While hand washing using cleansers is recommended by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as the best means to remove pathogens, frequent hand washing can cause dry and broken skin, increasing the user’s chance of infection and causing discomfort. Hand sanitizers are widely used by doctors and dentists as secondary means of pathogen reduction, but hand sanitizer use is recommended only when hands are not visibly soiled.
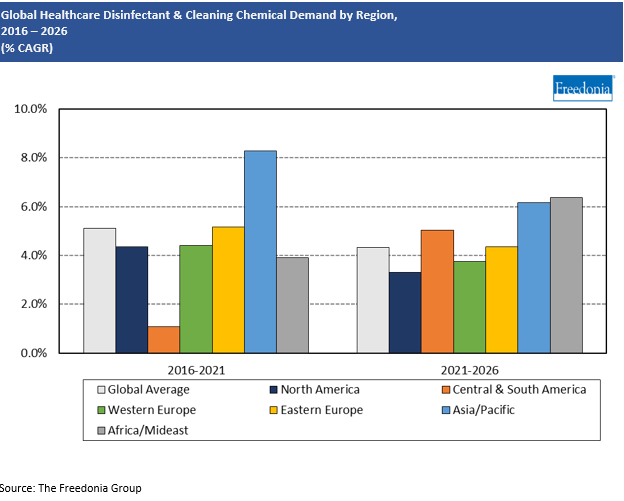
Demand by Region
Cleaning chemicals serve a vital purpose in the healthcare market due to the potential for the spread of highly infectious diseases in healthcare facilities (healthcare-associated infections, or HAIs) and other settings where large numbers of people congregate, eat, or live in close quarters.
Global demand for healthcare disinfectants and cleaning chemicals is expected to rise 4.3% annually to $4.6 billion in 2026. Growth will come off a high 2021 base, attributable to a combination of increased intensity/frequency of cleaning and sanitation related to the pandemic and a resumption of routine health and dental care visits. Gains will largely driven by:
- efforts to combat the threat of HAIs – including pneumonia and C. diff – and other health threats such as HIV/AIDS, MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), and hepatitis
- the expanding base of medical facilities, especially in developing regions where cleaning chemical usage has, in general, been lacking
- introductions of disinfectants that target broader ranges of pathogens
- the ongoing development of new techniques designed to stay ahead of such threats as the emergence of more resistant bacterial strains
As in other markets, the challenge for manufacturers serving the healthcare industry will be to develop products that comply with customer demands – including mildness, ease of use, and environmental safety – without compromising fundamental efficacy.
In addition, disposable medical devices and new, nonconventional sanitizing technologies like ultraviolet (UV) are expected to compete with chemical disinfecting products, although such technologies are more costly (at least initially) and their applications somewhat limited. Also restraining growth will be continuing efforts to shorten hospital stays and the greater prevalence of home healthcare organizations, which reduce the need for institutional cleaning chemicals.
The Asia/Pacific and Africa/Mideast regions are expected to see healthy growth, as the number of healthcare facilities increases, most notably in urban settings, to meet the needs of growing populations. Increasingly stringent cleaning and disinfection protocols in these regions will also benefit gains.