Report Overview
-
Conventional plastic straws continue to be replaced by new alternatives
-
Paper, bioplastic, and molded fiber straws all expected to see strong growth
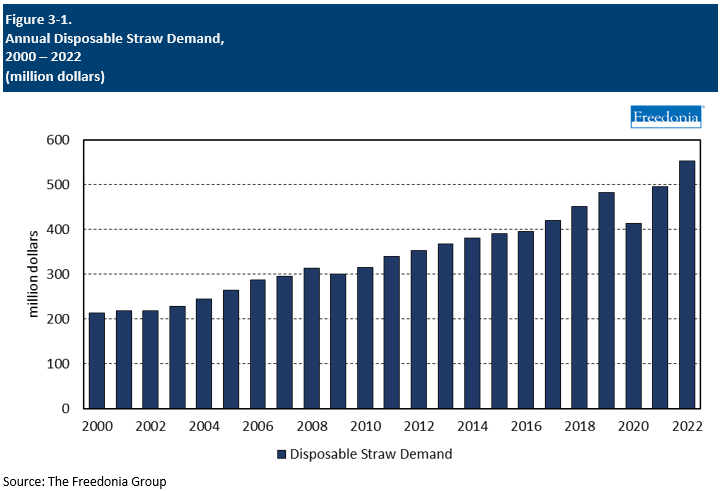
This Freedonia industry study analyzes the $553 million US disposable straw industry.  It presents historical demand data (2012, 2017, and 2022) and forecasts (2027 and 2032) by material (conventional plastic, bioplastic, paper, and molded fiber) and market (foodservice, consumer/retail, and beverage packaging). The study also evaluates company market share and competitive analysis on key industry competitors including Hoffmaster Group (Aardvark), D&W Fine Pack, WinCup, Pactiv Evergreen, and Fuling.
It presents historical demand data (2012, 2017, and 2022) and forecasts (2027 and 2032) by material (conventional plastic, bioplastic, paper, and molded fiber) and market (foodservice, consumer/retail, and beverage packaging). The study also evaluates company market share and competitive analysis on key industry competitors including Hoffmaster Group (Aardvark), D&W Fine Pack, WinCup, Pactiv Evergreen, and Fuling.
Featuring 56 tables and 16 figures – available in Excel and Powerpoint! Learn More This report includes data from 2012-2032 in 5 year intervals and tables featuring year-by-year data for 2019-2026.
The US market for disposable straws continues to face unprecedented disruption, with the lingering impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, sustainability initiatives, and bans on single-use plastics all combining to escalate changes in volume usage, pricing, and the types of materials used in produce straws. Foodservice is by far the largest market for straws and will continue to have an outsized impact on overall straw industry trends.
Demand for disposable straws is forecast to grow 1.5% annually to $597 million in 2027. However, this growth rate hides two opposing underlying trends:
- Growth in average prices will be supported by a transition from conventional plastics to higher value materials such as paper and bioplastics and this will support growth in market value.
- Demand in unit terms will decline as sustainability-driven efforts and bans aim to reduce or eliminate straw use.
Sustainability Becomes the Major Factor in Straw Choices
Historically, straw end users have generally valued performance and cost over sustainability in purchasing decisions. However, growing public awareness of the negative impacts of small plastic items like straws and expansion of single-use plastics bans have made plastic straws a target of sustainability initiatives, especially among foodservice leaders whose products are in the spotlight. This has resulted in:
- a strong push toward using biodegradable alternatives – such as paper, molded fiber, and bioplastics – instead of polypropylene
- efforts to reduce usage by only providing straws upon request or eliminating straws altogether by using alternatives such as strawless lids
New Materials Compete for Market Share as Conventional Plastic is Phased Out
As more consumers recognize the negative environmental effects of conventional plastic straws, they will continue to be replaced by new alternatives that have entered the market. However, there has yet to be a clear leader in the race to replace conventional plastic.
Initially, paper and polylactic acid (PLA) bioplastic straws were the most available products. However, paper’s performance issues inhibited early adoption while PLA received criticism for its lack of biodegradability. As a result, newer materials such as molded fiber and polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) bioplastic have recently entered the market, aiming to provide both good performance and strong environmental profiles.
US Straw Production Ramps Up as Alternative Materials Flourish
Historically, straws have largely been manufactured in Asia (mostly in China) and imported to the US. While straws can be expensive to ship long distances, China’s large low cost plastics industry allowed the country to be a dominant player in the US market despite shipping costs. However, plastic straw bans in China combined with temporary US tariffs led to an increase in domestic production, especially for paper and bioplastic straws.
Historical Market Trends
At its broadest level, demand for disposable straws is driven by trends in foodservice revenue, which is an indicator of the number of meals eaten away from home and the amount spent on those meals. Growth in foodservice activity in turn is dependent on a number of macroeconomic and demographic factors including:
- the health of the overall economy and levels of disposable income, which impact the ability of consumers to spend on more expensive restaurant meals (compared to home cooking)
- changes in the population mix, especially in terms of age cohorts (such as young adults) that are likely to eat out more often
- trends in consumer spending, including spending on travel and entertainment, which impact foodservice sales at hotels and sports and recreation venues
Beyond these basic macroeconomic indicators, other factors that can impact the foodservice industry and demand for disposable straws include:
- the share of total restaurant orders that are provided via drive-thru, curbside pickup, carryout, or delivery services
- the presence and diversity of drink options, as straws are mainly used for cold beverages such as soft drinks, iced coffee, and smoothies
- social factors such as health concerns, which not only influence the amount consumers eat out but their decision on whether to use a straw
- sustainability initiatives, which impact the overall level of straws used as well as the types of materials used
- regulations, especially restrictions on single-use plastics which often include straws
Historically, straw demand registered relatively steady growth, generally tracking foodservice beverage sales. However, around 2015, concern about the impact of small plastics on the environment and a growing sustainability movement began to impact industry sales.
Straw usage fell sharply in 2020 as the COVID-19 pandemic limited restaurant sales, with especially large losses in the full service restaurant and bar segment. While straw demand grew in 2021 and 2022 this was solely due to recovery in the foodservice sector, as use of straws per order continued to decline.
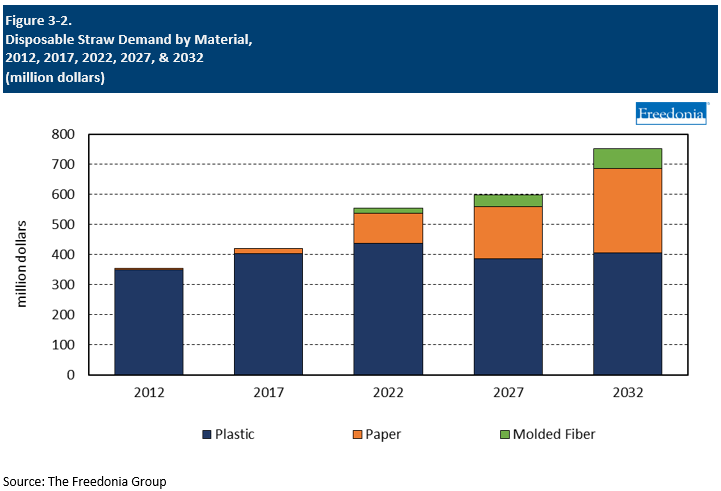
Demand by Material
Disposable straws can be made of a variety of materials including:
- conventional plastics, mainly polypropylene
- bioplastics, such as polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
- paper
- molded fiber from sugarcane, bamboo, wheat straw, and other plant sources
Demand for disposable straws in the US is forecast to rise 1.5% annually through 2027 to $597 million. Efforts to reduce straw use will result in overall declines in unit demand, all of which will be concentrated in conventional plastic straws. Straws made from alternative materials – especially newer bioplastic and molded fiber types – will see strong unit growth, and the higher average price of these new straws will push up overall market value:
- Plastic will continue to be the primary material used in the straw industry due to its combination of low cost and good performance. While demand for straws made from polypropylene and other conventional plastics will decline, overall use of plastic will be supported by strong growth in demand for bioplastic straws.
- Paper straw demand will continue to register above average growth as paper replaces conventional plastic straws in all markets. However, growth will lag that of other alternative straw materials due to the poor customer response to some early product introductions. Paper straw producers are working to address performance issues and develop improved adhesives and coatings that do not prevent biodegradability.
- Molded fiber straws are the newest entrant to the disposable straw market. Molded fiber straws have good market growth potential as they effectively balance sustainability and performance. However, prices need to decline in order for these straws to see widespread adoption.
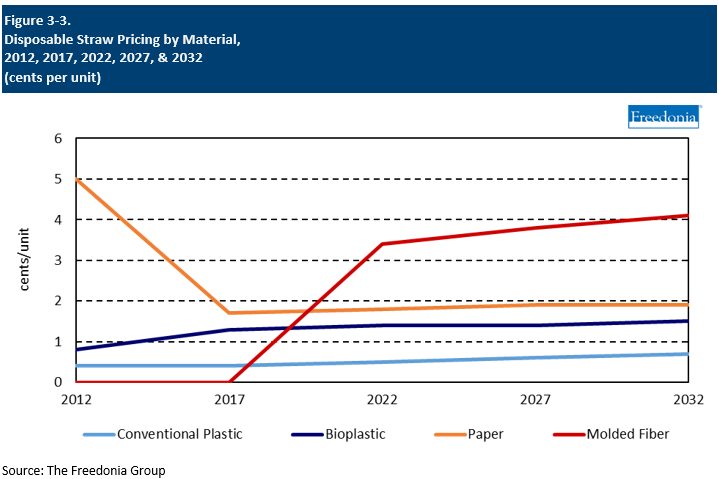
Pricing Trends
The disposable straws industry is competitive, and product pricing is a significant factor in customer purchasing decisions. Factors influencing prices for disposable straws include:
- raw material and labor costs
- shipping and transportation costs
- supply and demand balances
- customization, design, and printing costs
- changes in the material mix
- increasing participation in and corresponding competition from products made of newer and more innovative materials
- import competition
Raw material cost fluctuations tend to have the greatest effect on single product pricing, although a change in the product mix can have a strong impact on overall average price trends:
- The price of plastic straws is largely determined by the price of polypropylene, which, in turn, is affected by crude oil and natural gas prices.
- Paper straw prices are linked to the price of bleached and unbleached kraft paper and food grade paper.
Nonetheless, pricing for disposable straws does not always track raw material costs, as manufacturers tend to absorb raw material price increases as much as possible to maintain competitiveness.