Report Overview
 Where is e-bike production increasing?
Where is e-bike production increasing?
-
In recent years, Eastern Europe has evolved into a major e-bike production hub because of its lower manufacturing costs and proximity to major West European markets.
This Freedonia study analyzes the 28 million unit global e-bike market. The study presents demand figures for 2012, 2017, and 2022, and forecasts for 2027 and 2032. We also offer annual data for the 2019-2026 period and historical e-bike demand charts for the 2000-2022 period for all countries. Global E-Bikes provides data for 25 countries and two additional regions (Eastern Europe and the A/M region). This Freedonia study also provides market share for 13 leading suppliers, such as Accell Group, Aima Technology, Giant Manufacturing, Jangsu Yadea, Merida, Pon, and Yamaha.
Featuring 85 tables and 106 figures – available in Excel and Powerpoint! Learn More
Read the Blog: Government Legislation Incentivizing the Use of E-Bikes
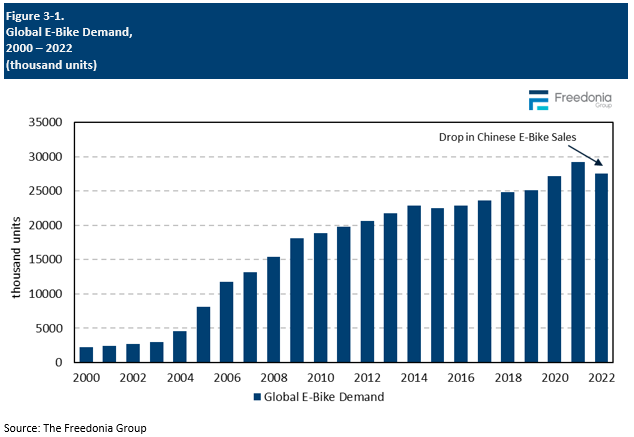
Global demand for e-bikes is forecast to expand 5.9% annually to 36.6 million units in 2027. This represents an acceleration from the 2017-2022 period as China – which accounts for two-thirds of global e-bike sales – rebounds following a significant, pandemic-induced drop in sales in 2022. Excluding China, e-bike sales will grow at an even faster pace, supported by the:
-
greater availability of these products globally as production increases and a wider range of models are offered, including high-performance models, for both transportation and recreation purposes
-
incentivization of e-bike usage through government subsidies and infrastructure
-
establishment of new e-bike sharing/rental programs in large cities
However, the size of the e-bike market will continue to be restrained by the underdeveloped electric grids of many lower income countries, which make electric vehicles less appealing. In addition, competition from electric scooters, mopeds, and motorbikes (which can offer better performance than e-bikes) will serve as a check against e-bikes in some markets.
China to Account for 42% of Global Market Gains through 2027
After contracting 12% in 2022 because of the country’s strict Zero-COVID policy and associated economic turmoil, sales of e-bikes in China – the world’s largest market for these products – are expected to rebound at a healthy pace through 2027. As one of the earlier adopters of e-bikes, China has significant replacement needs for these machines, which have become an essential mode of transportation. Improving product quality will also make e-bikes more competitive with other types of two-wheelers. Finally, the Chinese government will continue to actively promote the electrification of transportation and support the country’s massive e-bike industry.
Government Initiatives & Replacement Sales Boost Demand in Western Europe
Western Europe features a sizable stock of e-bikes, as the region was one of the first to see penetration of this technology. As such, replacement sales will account for some demand in countries such as Belgium, Germany, and the Netherlands, where e-bikes experienced earlier adoption. In other regional countries with less established e-bike markets, such as Spain and the UK, growth will come from riders transitioning from conventional bicycles to e-bikes. Sales will also be supported by government measures to lessen the environmental impact of transportation. For instance, in 2023, the EU announced a new strategy for cycling through 2030 that aims to promote cycling and encourage e-bike use, including investment in required charging infrastructure.
Historical Market Trends
The growing global e-bike market is affected by several related factors:
-
Historically, e-bike availability was limited in most parts of the world, but these machines have become an important mode of transportation in many nations in recent years as the quality of these bikes have improved.
-
Replacement product sales – which are highly cyclical – are a key driver of growth in mature markets such as Belgium, China, Germany, Japan, and the Netherlands.
-
The use of e-bikes in many countries is driven by government policies, including subsidies, regulatory changes, strategic investments, and other measures.
-
E-bikes have a fairly long lifespan, although considerations about performance can spur operators to replace a machine.
Among the other factors that can have a positive or negative impact on the global e-bike market’s growth cycles are:
-
economic conditions and level of international trade
-
changes in the value of a country’s currency
-
personal income and consumer spending trends
-
the increasing or decreasing availability of e-bikes and changes in prices
-
the introduction of new models that offer superior performance and have greater aesthetic appeal, which can spur both new and replacement sales
-
the adoption of new technical and safety standards, which can greatly drive up prices
Demographic and economic factors also greatly affect levels of demand for e-bikes in all countries and regions, as do less quantifiable factors such as the presence of a cycling culture and consumer preferences. The size and growth of the market for e-bikes in each country is affected by:
-
population growth and changes in the age distribution of its population
-
competition from other forms of transportation (such as bicycles, internal combustion engine – ICE – two wheelers, light vehicles, and public rail and bus transport)
-
riding conditions (e.g., quality of road, rules enforcement)
-
legal and regulatory environment (licensing and down payment requirements)
-
popularity of cycling, ranging from mountain-biking to racing to off-roading
As markets begin to develop, they typically see a prolonged period of growth (often exceeding 10 years) because of the potential size of the market. E-bikes compete directly with conventional bicycles, and tens of millions of these machines are sold globally. During the early stages of development, consumer preferences begin to evolve, and operators shift to more capable models, driving up prices. Government incentives have helped sustain long-term e-bike market growth.
Global E-Bikes in Use
There are more than 150 million e-bikes in use worldwide:
-
The Asia/Pacific region – led by China – accounts for the overwhelming majority of the e-bikes in use globally. The markets of multiple regional countries – particularly China, Japan, and Taiwan – were among the first to develop in the world. A handful of countries have seen dramatic growth in recent years (e.g., India).
-
Western Europe has the world’s second largest stock of e-bikes. Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands, and a few other countries feature more established e-bike markets and high e-bike ownership rates. Since 2017, e-bike sales have grown dramatically in most regional countries.
-
With the exception of North America (more specifically the US), most other regions have small stocks of e-bike. Demand for e-bikes in the US nearly quadrupled between 2017 and 2022, causing its e-bike parc to grow rapidly.
-
The underdeveloped electrical grids of many developing Central and South American and Africa/Mideast nations (as well as some Asia/Pacific countries), reduces the appeal of e-bikes and limits their use.
-
As Eastern Europe has become a large production hub for e-bikes since 2017, both its market and stock of e-bikes have grown rapidly.
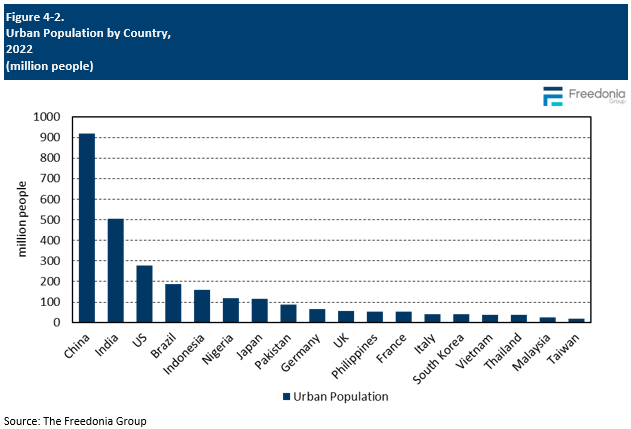
Urban Population Density
Typically, countries with significant urban populations – such as Germany, India, Japan – tend to have higher levels of e-bike sales because major densely populated cities tend to be important centers of product demand:
-
E-bikes and other two-wheelers are more convenient, faster, less expensive, and easier to navigate and park in these cities than automobiles.
-
Consumers in urban areas tend to have greater financial resources than their counterparts in rural areas.
-
A wider range of models are available in cities because more companies serve these areas.
-
Cities are more likely to have the required charging infrastructure for e-bikes, as well as electric motorcycles, scooters, and mopeds.
-
The quality of roads tend to be better in cities around the world.
-
Two-wheeler rental businesses and sharing programs are only typically found in large cities.
-
Businesses in urban areas are more likely to use e-bikes.
Competitive Product Trends (Light Vehicles & Bicycles)
E-bikes compete directly with:
-
conventional bicycles
-
internal combustion engine scooters and mopeds, and to a lesser extent, light motorcycles
-
electric scooters, mopeds, and motorcycles
Many conventional bicycle riders have upgraded to electric models because they offer greater convenience and can travel greater distances at higher speeds. However, e-bikes are generally more expensive than conventional bicycles.
Because higher end e-bikes offer superior performance, they are able to compete with some ICE and electric scooters and mopeds, particularly in densely populated cities. E-bikes have captured market share from these products in some countries because they are less expensive and generally do not require insurance or a license. They are also less expensive to maintain and easier to operate. Nonetheless, global demand for ICE scooters, mopeds, and motorcycles remains well above that for e-bikes because they are more established products.