Report Overview
Highlights: Industrial Fasteners Market Trends
- Market growth: The global industrial fasteners market is projected to grow 4.7% per year to reach $119 billion in 2027, driven by a rise in manufacturing activity.
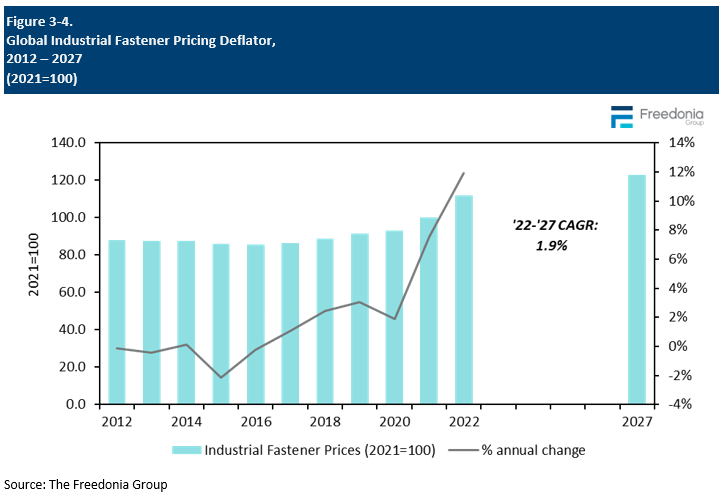
- Price shifts: Industrial fastener prices are expected to increase 1.9% annually until 2027. This represents a notable slowdown in price escalation compared to the previous period from 2017 to 2022.
- Regional dynamics: The Asia/Pacific region plays a significant role as a major net exporter of industrial fasteners. Its share of global production is anticipated to increase in the future.
New Industrial Fasteners Industry Analysis
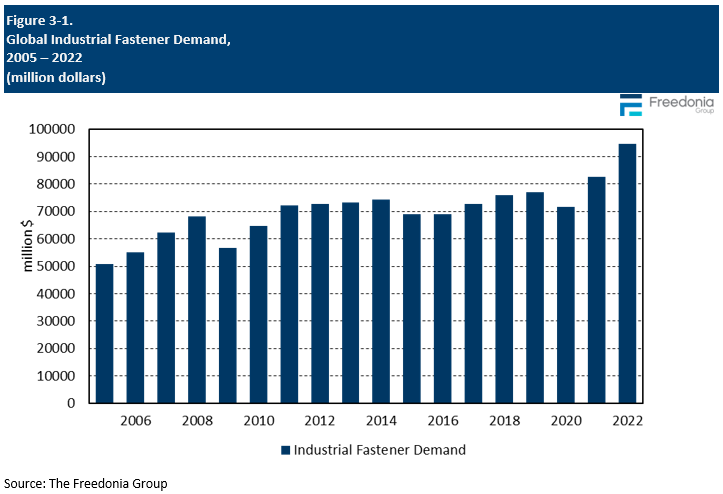
This Freedonia industry study analyzes the $95 billion global industrial fasteners industry. It presents historical demand data (2012, 2017, and 2022) and forecasts (2027 and 2032) by product (standard-grade fasteners, aerospace-grade fasteners), market (original equipment manufacturing, maintenance/repair/operations, construction), and region (North America, Central and South America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Asia/Pacific, Africa/Mideast). The study also evaluates company market share and competitive analysis on industry competitors including Berkshire Hathaway, ITW, LISI, Nifco, and Stanley Black & Decker.
Featuring 202 tables and 98 figures – available in Excel and Powerpoint! Learn More
This report includes data from 2011-2031 in 5 year intervals and tables featuring year-by-year data for 2018-2025.
See the top 5 Industrial Fastener Statistics.
Global demand for industrial fasteners is forecast to increase 4.7% per year to $119 billion in 2027. Market value will be driven by an acceleration in real demand growth due to expanding manufacturing activity worldwide. However, a slowdown in pricing growth relative to the highly inflated 2017-2022 period will temper the pace of gains somewhat.
OEM Motor Vehicle Market Poised for Strong Rebound
The motor vehicle manufacturing market – the largest global outlet for fastener sales – significantly underperformed most other industrial fastener markets during the 2017-2022 period. Demand was hampered by supply chain issues associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, most notably the global automotive chip shortage. Insufficient component supply significantly limited motor vehicle production from 2020 through 2022, leaving producers unable to meet demand.
While the chip shortage has yet to be fully resolved as of July 2023, this issue is expected to ease significantly as 2023 progresses and cease to be major constraint by 2025. As a result, automakers will rapidly step up production to meet pent-up demand, driving strong growth in related fastener sales. Advances in the motor vehicle market will be further supported by the ongoing transition to electric vehicles, which will require expanded collaboration between fastener suppliers and automakers to develop products for new vehicle platforms.
Recent Industrial Fasteners Pricing Trends
Industrial fastener markets have, in recent years, been plagued by volatility in raw materials prices; steel, in particular, spiked in 2021 and 2022 and precipitated elevated fastener price growth in those years. At the global level, this served to expand the market’s value because OEMs who rely on fasteners had little recourse but to keep buying regardless of cost. However, this intensified the role of pricing pressures in shaping the market and accelerated manufacturing shifts from high-income European countries to Asian nations.
Materials and energy prices generally began to stabilize in the second half of 2022, returning to levels that more closely resembled those from the years leading up to the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result, price growth is expected to slow significantly going forward. However, the inflationary pressures associated with the pandemic have largely been internalized into supply chains – e.g., via increased labor costs – and fastener prices are not expected to return to pre-2020 levels.
Production Increasingly Shifting to Asia/Pacific Region
The Asia/Pacific region is a massive net exporter of industrial fasteners, and its share of global production is expected to rise going forward. Production is supported by strong materials supply since China and a handful of other countries in the region dominate global steel production. Higher-income countries like the US are engaged in efforts to support their domestic fastener industries, partly due to greater concerns over supply chain security following pandemic-related disruptions. As a result, fastener trade between China, the US, and the EU will continue to be impacted by government attempts to regulate trade. However, the fundamentals of material supply mean that non-Asian nations will face significant challenges in swaying production elsewhere.
Historical Fasteners Market Trends
Industrial fastener demand is cyclical because most of these products are used in industries that are cyclical themselves. In 2022, for example, 76% of global industrial fastener demand was accounted for by sales to manufacturers of motor vehicles, machinery, aerospace equipment, fabricated metal products, and electrical and electronic products.
Furthermore, the commodity-like, nondifferentiated nature of many types of fasteners compounds their cyclicality:
- Fasteners, like most commodity products, can be mass produced.
- Equipment manufacturers can stockpile large inventories in anticipation of demand that may or may not materialize.
- When demand for durable goods increases suddenly – as is typical following the troughs of recessions or slowdowns within expansions – OEMs may find themselves without sufficient components inventory, causing demand for fasteners to surge.
The critical nature of fasteners as components also tends to tie demand tightly to conditions in underlying manufacturing markets. While fasteners compete to an extent with several alternative joining technologies – such as adhesives, welding, and mechanical joining – it is typically impractical functional reasons to significantly reduce or increase usage of fasteners in product designs in response to short-term economic conditions.
The broad range of products in which fasteners are used and their sizable replacement market does serve to protect industrial fastener suppliers from the swings in the business cycle to a certain degree. However, maintenance and repair fastener markets tend to account for a smaller share of demand than those in other component-supplying businesses because many types of fasteners are designed to last the lifetime of the product or structure in which they are originally installed.
In addition, many fastener manufacturers – particularly the numerous smaller firms – specialize in a limited range of products and market niches, making them more susceptible to changes in business conditions.
The market for fasteners is also impacted by volatility in materials and energy costs, especially as the nature of these products means that materials costs account for a high share of production costs. In times of high materials costs, fastener prices tend to increase rapidly, expanding the size of the market in nominal terms.
Industrial Fasteners Market Demand by Material
Industrial fasteners are produced using various metals and alloys and a wide range of plastic resins. Steel and stainless steel dominate, accounting for 75% of demand in 2022. Plastics comprised 14%, while aluminum, copper-based, and other nonferrous metals collectively made up the remaining 11%.
The dominance of steel is driven by the material’s strength and durability, which makes it an ideal choice for critical components designed to last through the life of a product. While volatility in iron and steel prices can pose issues for fastener manufacturers and their customers, firms can address this by attempting to stockpile material supplies in periods of relatively low prices. Steel fasteners are commonly produced using cold head quality (CHQ) steel, and this will remain the leading material type going forward.
The primary advantage of plastic fasteners is their low weight, which makes them a desirable option for manufacturers attempting to reduce the weight of their products. In particular, demand for plastic fasteners has been driven by lightweighting efforts in the motor vehicle industry, with suppliers developing a wide range of screws, rivets, and application-specific fasteners for use in automotive applications. Plastic fastener demand was impacted by the underperformance of the motor vehicle industry, but it is projected to post strong growth as automotive manufacturing rebounds through 2027. Plastic fasteners are also widely used in electronics manufacturing due to their absence of electrical conductivity.
Copper-based products represent the bulk of fasteners made from nonferrous metals. Key features of copper-based fasteners are their strong corrosion resistance and high electrical conductivity. As a result, they are commonly used in the maritime and electronics industries.
Other alternative metals include aluminum and titanium:
- Aluminum offers the benefit of light weight, but it has issues with corrosion when in contact with other metals.
- Titanium fasteners offer exceptional performance, but they are expensive. Consequently, their use is limited to higher-end applications, with the aerospace equipment industry representing the most important user of these products.
Pricing Patterns for Industrial Fasteners
Industrial fastener prices vary widely depending on fastener type, material, intended application, and performance characteristics:
- Small commodity-type fasteners designed for noncritical applications are extremely inexpensive, costing less than $0.01 each when purchased in bulk.
- Prices of heavier duty standard-grade items can be $1 or more.
- Specialty – and especially aerospace-grade – fasteners engineered for use in harsh environmental and performance-critical settings are the most expensive, typically costing more than $2 each.
- Extremely large fasteners used in nonbuilding construction are much more expensive than most other products, with average per unit prices of well over $10.
A major factor impacting average fastener prices is the cost of raw materials used in their production. Raw material costs can account for as much as 70% of total production costs, and prices of commodity-grade fasteners are thus highly susceptible to changes in materials costs. However, the industry is insulated from this volatility to an extent by long-term supply contracts between materials suppliers, fastener manufacturers, and their customers. As a result, the impact of materials price changes on fastener prices tends to play out over a longer timescale.
Aerospace-grade fastener prices tend to be more volatile than standard-grade types, as:
- There are a relatively small number of suppliers in the market, which allows aerospace-grade manufacturers considerable latitude to raise prices in response to changes in their own cost structure.
- As aircraft manufacturers have limited sourcing options, prices increase significantly when there are shortages in the market. This contributed to elevated price growth in 2022 as aerospace equipment manufacturing began to rebound following two years of depressed industry activity.
Like many other industries, the global fasteners industry exhibited atypically high levels of price growth in the years following the COVID-19 pandemic. High prices of materials like iron and steel were the main driver of price hikes; other factors included:
- high energy costs, which were reflected to an extent in materials costs
- supply chain issues, such as elevated prices for international shipping
Global average prices for industrial fasteners are forecast to increase 1.9% per year through 2027, marking a significant moderation in price growth compared to the 2017-2022 period.
Both standard-grade and aerospace-grade fastener prices are expected to register increases through 2027. Price gains will be supported by:
- increased demand for new, higher value products
- rising demand in many OEM markets
However, ongoing intense competition from producers in developing countries, which compete heavily with local producers on price, will serve to temper the pace of gains.